ZROI 2022CSP7连测 Round1 解题报告
100 + 30 + 70 + 0,rk 32.
$\log^2 n$ 被卡常,哈哈。
A
考虑把 $k$ 分解质因数,设 $k = \prod p_i^{c_i}$,那么任何一个合法的答案 $n$ 应当满足 $\exist c_j < c_i,2c_j \geq c_i$。
题目要求的是最小,所以我们并不需要考虑 $p_i$ 以外的质因子,上边的方法已经给出了构造方案,直接构造即可。
1 | ll x,n; |
B
算法 1
对于 $a_i \leq 3$ 的情况,其实等于一个多重集排列,直接计算即可。
算法 2
题目中给出了一个很强的性质:$1 \leq a_i \leq 9$,所以我们只需要对 $9$ 种情况进行讨论。
对于 $1,5,7$ ,由于他们和其他数都互质,所以他们可以去任何位置。最后再考虑。
对于 $6$,我们发现它与其他数都不互质,无法交换,所以我们把 $6$ 视为分界点,分段进行考虑。
对于 $2,4,8$ 以及 $3,9$ 这些数之间是不能随便移动的,相对顺序相同。两类的数可以交换,记第一类个数为 $a$,第二类为 $b$,那么方案数就是 $\binom{a}{a+b}$,剩下的直接插板法做一下就行了。
1 | const ll mod = 998244353; |
C
算法 1
通过暴力/直觉发现答案具有凹性,直接大力三分出目标值,暴力计算时间复杂度是 $\mathcal{O}(n^2\log n)$ 的。
算法2
思考我们能不能优化查询的过程,我们发现计算权值的本质可以分为两个部分:小于 $val$ 的和大于 $val$ 的。对于两个部分,我们开一个权值线段树维护,每次就查询一下和以及数的个数,时间复杂度 $\mathcal{O}(n\log^2 n)$。被卡常了。
这里的实现是一种不同于场上实现的较快的三分写法。
1 | const int N = 1e5 + 10; |
算法3
线段树部分到头了,我们考虑两个点变化的时候挪动的个数非常有限,事实上可以证明至多只会变 $1$。所以我们时间复杂度就是 $\mathcal{O}(n\log n)$。贴一个其他老哥写的 code
1 |
|
D
我们考虑这个东西怎么分开来计算,显然对于一个 $(x,y)$,我们计算的部分可以这么构成:
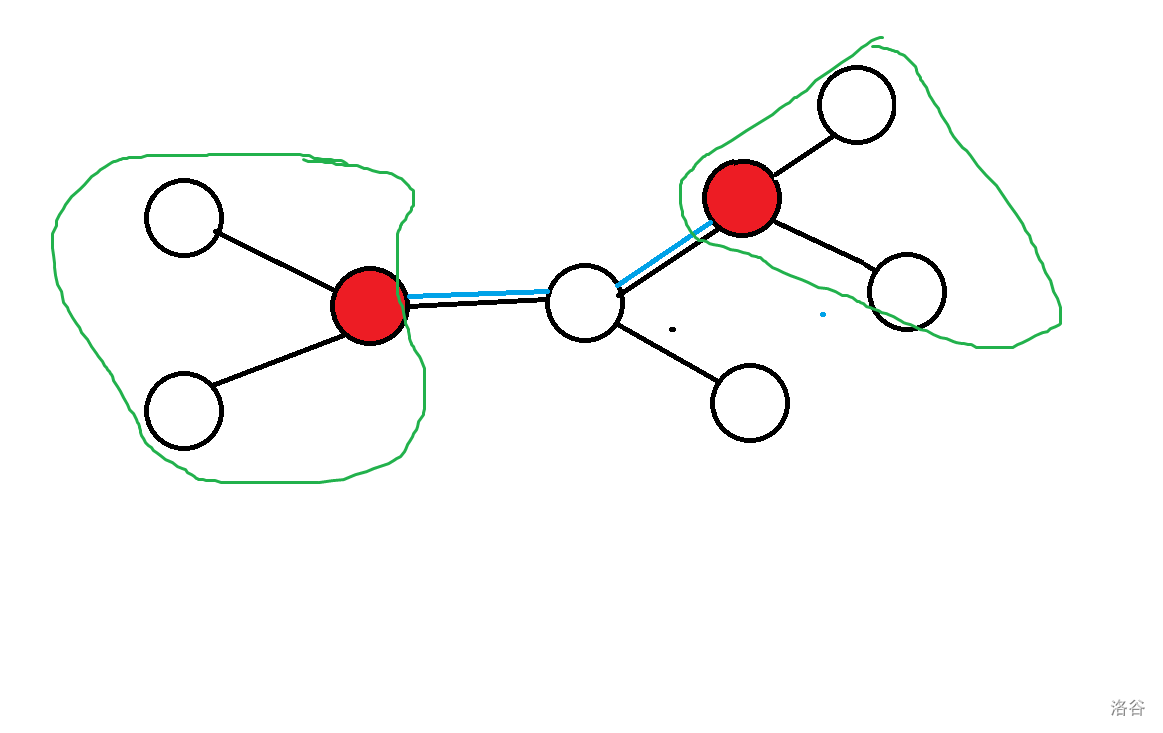
我们记 $f_{x,y}$ 表示树根为 $y$,以 $x$ 为根的子树内答案,那么答案就是 $f_{x,y} \times f_{y,x} \times dis_{x,y}$,暴力计算是 $\mathcal{O}(n^2 q)$ 的,我们考虑优化这个过程。
首先我们考虑,实际上我们并不是对于每一种询问都需要重新计算 $f$,只有一种情况我们需要特殊考虑:$x$ 在 $y$ 的子树内,以下我们称这种情况为包含情况。
对于不包含情况,我们实际上不需要处理额外的 $f$,我们直接按照定义处理出 $f_{x,1}$ 然后相乘就行了。正确性是显然的。
对于包含情况,可以看图理解一下:
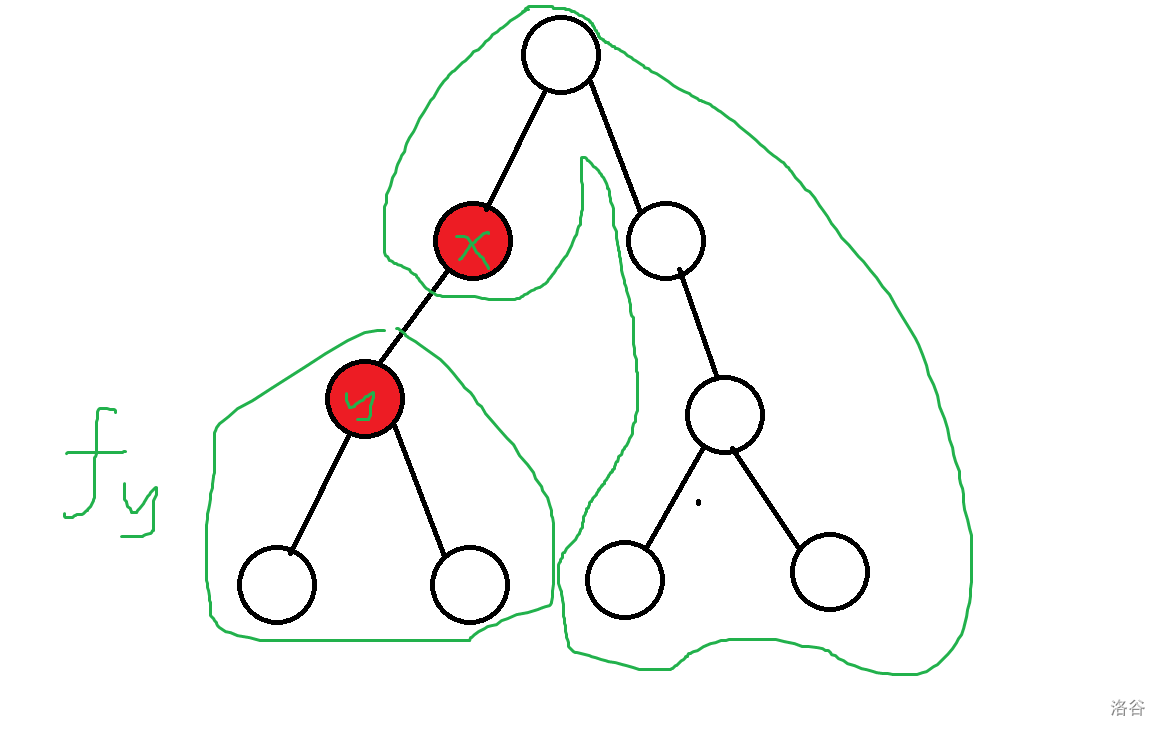
我们要计算的答案显然是两个绿色部分相乘,那么我们发现常规来计算 $x$ 的贡献是相对困难的,我们需要额外处理的是一个 $g$,它表示以当前节点 $x$ 的父亲为根时,除了 $x$ 子树内的答案。那么我们首先应该找到 $y$ 对应的 $x$ 的子树是哪一棵,这个我们可以通过暴力跳重链在 $\mathcal{O}(\log n)$ 的时间内做到。然后就统计一下即可。实现到代码是这样的:
1 | int get(int x,int y) { |
所以我们就在 $\mathcal{O}((n + q)\log n)$ 的时间内解决了问题,如果想要更快需要 tarjan 求 LCA,但是我猜没几个人写。
1 | inline int add(int x, int y) {return (x += y) >= mod ? x - mod : x;} |
ZROI 2022CSP7连测 Round1 解题报告